
The expression above says that 1 part of a small number (ppm) equals 1,000 parts of a smaller number (ppb) which equals 1,000,000 parts of an even smaller number (ppt. A simple exercise can help with understanding the different ways to express the amount of contaminant in water supplies. Definition: In relation to the base unit of density > (kilograms per cubic meter), 1 Grams Per Milliliter (g/ml) is equal to 1000 kilograms-per-cubic. In your case it looks like you have a density going in of 1.22mg per cc, and coming out of 1. Always check the results rounding errors may occur. Specific gravity is the ratio of the density of any substance to the density of water (1000 kilograms per cubic meter, or one gram per cc).
#How to calculate ppm from grams per liter how to#
If a fertilizer of 200 ppm nitrogen is desired, then: Advertisement. How to convert Grams Per Milliliter to Parts Per Million (g/ml to ppm) 1 g/ml 1000000 ppm. 3) Now using the molar mass to work out the molarity (moles per litre): Moles in one liter mass/molar mass 0.00289/522 5. Most water quality standards are expressed in ppm or milligrams per liter (mg/L), but many are expressed in ppb or micrograms per liter (ug/L), and a few are expressed in ppt or nanograms per liter (ng/L). Determine the mass (in grams) of fertilizer to dissolve per liter of water to achieve the desired ppm value by dividing by the percent (in decimal form) of the desired nutrient, then divide by 1,000. 2.89 ppm 2.89 g per 1,000 L 0.00289 g per 1 L If you work out the mass per liter it makes working out the next steps a little easier, because the final units for molarity will be mol/L. See the table below for other examples of percent concentration to ppm equivalents.Īnother concept that needs to be addressed is the difference between ppm, parts per billion (ppb), and parts per trillion (ppt.) As water quality regulations become more stringent and laboratory analysis techniques get better and better, contaminants are being identified at lower and lower levels. Divide the value you just obtained by the density of your solution in grams per millilitre. For example, if your solution is 250 ug/L, you would divide 250 by 1000 to get 0.250 ug/ml. In other words, just multiply the percent solution by 10,000 to calculate ppm. Because a litre (L) is equal to 1000 millilitres (ml), this calculation will give you the concentration value in units of micrograms per millilitre. This translates a 1% solution concentration to 10,000 ppm. A scientist wants to make 400 mL of 35 ppt. If you divide 1,000,000 or 1 ppm by 100 or 100% you get the following. The following equation is for a 35 ppt salinity solution containing 35 grams of salt per 1000 grams of saltwater.

Therefore, it shouldn’t be too difficult to convert percentage to ppm and ppm to percentage.

A solution with 1 M concentration would have 35.5 g of chloride per 1 L of solution. For instance, chloride has a molar mass of 35.5.
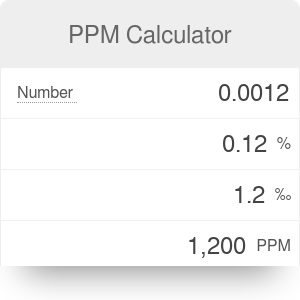
To convert from molarity to ppm, first determine the molar mass of a substance. In most cases, the two are considered equal. Most of the time, chemical concentrations are expressed in percentages (parts per hundred, pph.) However, in chemical dosage related problems, concentrations are expressed in ppm. For dilute solutions, one part per million equals one mg/L. It is important to understand the relationship between percentage and parts per million (ppm).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
